Internal Linking
Link Building Best Practices
Essential Guidelines for Effective Internal Link Building
Internal links form the foundation of effective on-page optimization and SEO. They play a crucial role in enabling Google to discover, crawl, and index pages within your website.
Without well-planned internal linking, certain pages may remain undiscovered by search engines, resulting in limited organic traffic. Moreover, a disorganized internal link structure can lead to a poor user experience, as visitors struggle to navigate your site and find relevant content.
By implementing strategic internal linking practices, you can not only increase the visibility of your pages in search results but also channel authority from one page to another, enhancing overall SEO performance.
So, let’s delve into the strategies for creating effective internal links, empowering your website to rank higher, expand its online presence, and ensure seamless navigation for users and search engines alike. Ready to get started? Let’s dive in!
What are internal links?
Internal links, from the perspective of Tajotec SEO agency, are the connective tissue of a website, facilitating navigation between different pages within the same domain. These links are hyperlinks that point from one page on a domain to another page on the same domain. They serve as pathways for both users and search engine crawlers, allowing them to explore and access various sections and content on the website.
Internally linking relevant pages within a website not only enhances user experience by guiding visitors to related or supplementary information but also plays a vital role in SEO. By strategically incorporating internal links, Tajotec ensures that valuable pages receive proper visibility, authority, and indexing by search engines like Google. This approach strengthens the overall structure of the website, improves its organic search rankings, and contributes to a more seamless browsing experience for visitors.
Why are internal links important for SEO?
Internal links are crucial for SEO for several reasons:
- Crawlability: Internal links help search engine crawlers discover and navigate through different pages on your website. By providing clear pathways between pages, you ensure that all content is accessible and indexed by search engines.
- Indexing: When search engines crawl your website, they follow internal links to index pages. Pages that are not internally linked may not be indexed, resulting in them not appearing in search results.
- Page Authority: Internal linking allows you to distribute page authority (also known as link equity) throughout your website. By linking from high-authority pages to other relevant pages, you pass on authority and help those pages rank better in search results.
- Keyword Relevance: Anchor text used in internal links provides context to search engines about the content of the linked page. By using relevant keywords in anchor text, you can signal to search engines the topic or theme of the linked page, which can improve its relevance for specific search queries.
- User Experience: Well-structured internal linking enhances the user experience by guiding visitors to related content or additional resources they may find valuable. This can increase engagement, reduce bounce rates, and encourage visitors to explore more pages on your website.
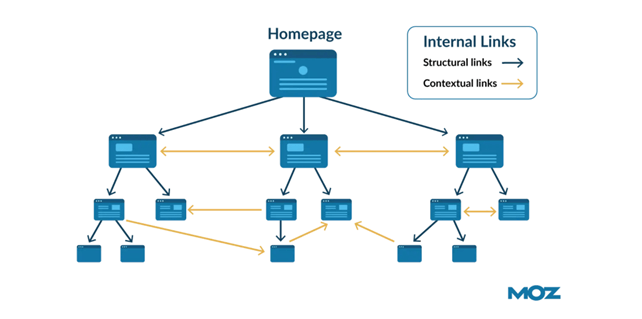
Look at this image from Moz resource to explore correct internal linking:
Overall, internal links play a critical role in optimizing your website for search engines and improving the visibility, authority, and usability of your content.
Types of internal links
Internal links on a website serve various purposes and can be categorized into different types based on their functionality and placement. Here are some common types of internal links:
- Navigation Links: These are links typically found in the main navigation menu, footer, or sidebar of a website. They help users navigate between different sections or pages of the site, such as Home, About Us, Services, Contact, etc.
- Contextual Links: Contextual links are embedded within the content of a webpage and provide additional information or resources related to the topic being discussed. They enhance the user experience by offering relevant content without disrupting the flow of the main content.
- Breadcrumb Links: Breadcrumb navigation consists of a series of links that show the hierarchical structure of the website and indicate the user’s current location within that structure. They help users understand the relationship between pages and easily navigate back to higher-level categories.
- Related Posts/Articles Links: These links appear at the end of a blog post or article and suggest other relevant posts or articles that readers may be interested in. They encourage further exploration of the website’s content and can increase engagement.
- Footer Links: Links placed in the footer section of a website often include important pages like Privacy Policy, Terms of Service, Sitemap, etc. They provide additional navigation options and ensure that essential pages are easily accessible to users.
- Internal Search Links: If a website has a search functionality, internal search links appear in search results, allowing users to navigate directly to specific pages or content within the site.
- Anchor Links: Anchor links, also known as jump links or in-page links, are used to navigate to different sections of the same webpage. They are especially useful for long-form content where users may want to jump to specific sections quickly.
By strategically incorporating these types of internal links throughout a website, webmasters can improve navigation, enhance user experience, and optimize the site’s structure for both users and search engines.
Top 10 SEO best practices for internal link building
Internal link building is a crucial aspect of SEO that can significantly impact the visibility and ranking of your website on search engine results pages (SERPs). Here are some top SEO best practices for internal link building:
- Create a Logical Site Structure: Before you start building internal links, ensure that your website has a clear and logical structure. Organize your content into categories and subcategories, making it easier for users and search engines to navigate.

- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. Use descriptive and relevant anchor text that accurately describes the content of the linked page. Avoid generic phrases like “click here” and instead use keywords that reflect the topic of the linked page.
- Prioritize Relevance: Link to pages that are contextually relevant to the content of the linking page. Internal links should provide additional value to users by directing them to related or complementary content that enhances their understanding of the topic.
- Diversify Anchor Text: While using keywords in anchor text is important for SEO, avoid over-optimization by diversifying your anchor text. Use a mix of exact match, partial match, and branded anchor text to create a natural link profile.
- Optimize Your Homepage: The homepage is typically the most authoritative page on your website. Use it to strategically link to important category pages, top-level content, or cornerstone pages to distribute link equity throughout your site.
- Implement Breadcrumb Navigation: Breadcrumb navigation not only improves user experience but also provides an additional opportunity for internal linking. Include keyword-rich anchor text in your breadcrumb links to reinforce the topical relevance of your pages.
- Audit and Update Old Content: Regularly audit your website’s content to identify opportunities for internal linking. Update old or outdated content with new links to relevant pages, ensuring that your internal linking content strategy remains up-to-date.
- Avoid Overlinking: While internal linking is important, avoid excessive linking within your content. Focus on quality over quantity and only include links that add value to the user experience.
- Monitor Internal Link Performance: Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track the performance of your internal links. Monitor metrics such as click-through rates, bounce rates, and time on page to assess the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to a successful internal linking strategy. Develop a standardized approach to internal linking and ensure that all new content follows the same linking practices.
By following these best practices, you can improve the internal linking structure of your website, enhance user experience, and boost your SEO efforts.
Implementing Internal Links on Your Site
Implementing internal links on your website is crucial for enhancing user experience and optimizing your site for search engines. One aspect of effective internal linking is ensuring that your links are correctly formatted. Here’s a guide to the format for a correctly formatted internal link:
- Anchor Text: Ensure that your anchor text accurately describes the linked page’s content. Use relevant keywords to provide context. For instance: This link will take users to the services page of the Tajotec website.

- HTML Link Tag: Use the <a> tag to create internal links. Here’s an example: This link will take users to the blog page within the Tajotec website.

- Relative URLs: When linking to pages within the same website, you can use relative URLs. For example: This link will take users to the contact page of the Tajotec website.

- Absolute URLs: If linking to pages on another website or specifying the full path, use absolute URLs. Example: This link will take users to a page on an external website.

- Open in New Tab: Optionally, you can have links open in a new tab using the target=”_blank” attribute. For instance: This will open the “About” page of the Tajotec website in a new browser tab.

These examples demonstrate how to correctly format internal links on the Tajotec website, ensuring optimal user experience and SEO benefits.
Use Internal Links That Prompt Visitors to Act
In the realm of digital marketing, the utilization of internal links as Calls-to-Action (CTAs) is a strategic maneuver to prompt visitors to take specific actions, thereby enhancing engagement and driving conversions. These internal links serve as subtle yet powerful invitations, guiding visitors towards desired outcomes and fostering meaningful interactions.
Effective CTAs are seamlessly integrated within the content, strategically positioned to capture the visitor’s attention and encourage action. Here’s how you can leverage internal links as CTAs to prompt visitors to act:
- Learn More: Encourage visitors to delve deeper into your offerings by providing internal links to relevant product pages, informative articles, or resources.
- Contact Us: Prompt visitors to reach out for assistance or inquiries by directing them to your contact page.
- Subscribe Now: Invite visitors to subscribe to your newsletter or mailing list for exclusive updates and offers.
- Start Free Trial: Encourage visitors to experience your product or service with a risk-free trial.
- Shop Now: Direct visitors to your online store, enticing them to explore and make a purchase.
- Work With Us: Interested in partnering with us? Explore opportunities to collaborate and grow together.

By strategically incorporating these internal links as CTAs within your content, you provide visitors with clear pathways to take action, whether it’s exploring your offerings, contacting your team, or making a purchase. Remember, compelling CTAs not only drive engagement but also pave the way for meaningful interactions and conversions.
FAQ
Dofollow VS Nofollow Links
All links, whether internal or external, fall into one of two categories: dofollow or nofollow.
In essence, a dofollow link signals to Googlebot to transfer page authority or link juice to the linked page. Search engines follow dofollow links, indicating trust in the linked content.
Fortunately, dofollow is the default setting for most links, requiring no additional action to designate them as such.
Conversely, nofollow links instruct Googlebot not to pass link juice to the linked page. Search engines do not follow these links, suggesting a lack of full trust in the linked content.
To implement a nofollow link, you must adjust the link’s HTML code, as follows:

In nearly all cases of internal linking, it’s advisable to use dofollow links.
The only scenario where you might employ nofollow internal links is when you wish to prevent a page from being indexed by Google. In such instances, you would apply the nofollow attribute to every link leading to that page, alongside implementing a “noindex” directive for the page itself.