Technical SEO
Elevate Your Online Foundation
Empower Your Website with Expert Technical SEO Solutions
Think of search engine optimization (SEO) as the construction of a house: Technical SEO lays the foundation, ensuring structural integrity. On-page SEO builds the framework, shaping the structure and layout. Off-page SEO adds the finishing touches, enhancing the appeal and visibility. Each component is essential, much like removing the foundation would cause the entire house to crumble.

TajoTec’s technical SEO expertise is truly commendable. Their meticulous attention to detail and deep understanding of search engine algorithms have significantly improved our website’s performance. With their assistance, we’ve seen noticeable enhancements in site speed, crawlability, and indexability. Their team’s proactive approach and innovative solutions have made them invaluable partners in our digital marketing journey. I highly recommend TajoTec to anyone seeking top-notch technical SEO services.
What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website for search engine crawling and indexing. It involves making improvements to the technical aspects of a website to enhance its visibility and accessibility to search engines. This includes tasks such as optimizing website speed, improving site structure and navigation, fixing crawl errors, implementing schema markup, optimizing robots.txt and XML s, and ensuring mobile-friendliness, among others. The goal of technical SEO is to ensure that a website is technically sound and optimized for search engine algorithms, ultimately leading to higher rankings and better visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The beginner’s guide to technical SEO
In the vast landscape of digital marketing, technical SEO stands as the cornerstone of website optimization, playing a pivotal role in determining a site’s search engine visibility and overall performance. For newcomers venturing into the realm of search engine optimization (SEO), understanding the fundamentals of technical SEO is essential for laying a solid foundation for success.
Technical SEO encompasses a myriad of practices aimed at enhancing a website’s technical infrastructure to make it more crawlable, indexable, and user-friendly for search engines. From optimizing website speed and improving site architecture to fixing crawl errors and implementing structured data markup, technical SEO involves a comprehensive approach to fine-tuning the technical elements of a website.
In this beginner’s guide to technical SEO, we’ll delve into the core concepts and best practices that every novice SEO enthusiast should know. We’ll explore topics such as website speed optimization, mobile responsiveness, URL structure, canonicalization, and more. By gaining a deeper understanding of technical SEO principles, beginners can equip themselves with the knowledge and tools needed to optimize their websites for improved search engine visibility and user experience.
Whether you’re a business owner looking to enhance your online presence or a digital marketer seeking to sharpen your SEO skills, this guide will serve as your roadmap to mastering the essentials of technical SEO and laying the groundwork for long-term success in the competitive digital landscape.
Why is technical SEO important?
Technical SEO is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved Website Performance: By optimizing technical aspects such as website speed, mobile responsiveness, and site architecture, technical SEO ensures a smoother user experience. A fast-loading, mobile-friendly website is more likely to engage visitors and reduce bounce rates.
- Enhanced Search Engine Visibility: Search engines prioritize websites that are technically sound and easy to crawl. By addressing technical issues like crawl errors, duplicate content, and broken links, technical SEO helps search engines understand and index your website more effectively, leading to higher search engine rankings.
- Better User Experience: Technical SEO practices, such as optimizing site navigation and implementing structured data markup, contribute to a more user-friendly website. This enhances user satisfaction, encourages longer dwell times, and increases the likelihood of conversion.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s competitive online landscape, having a technically optimized website can give you an edge over competitors. Websites that load quickly, rank higher in search results, and provide a seamless user experience are more likely to attract and retain visitors.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Investing in technical SEO ensures the long-term health and sustainability of your website. By regularly monitoring and optimizing technical aspects, you can future-proof your site against algorithm updates and technological advancements, maintaining its performance and relevance over time.
Technical SEO checklist
Technical SEO checklist to ensure your website is optimized for search engines:
- Site Speed Optimization:
- Minimize server response time.
- Enable browser caching.
- Compress images and files to reduce load times.
- Utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for faster content delivery.
- Mobile-Friendliness:
- Ensure your website is responsive and displays properly on all devices.
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to verify mobile compatibility.
- Optimize font sizes, button sizes, and tap targets for mobile users.
- Website Security:
- Implement HTTPS protocol to encrypt data transmission.
- Install SSL certificates to secure connections.
- Regularly update security patches and software versions.
- Crawlability and Indexability:
- Create and submit a sitemap to search engines.
- Optimize robots.txt file to control crawler access to site resources.
- Check for crawl errors using Google Search Console.
- URL Structure:
- Use descriptive and SEO-friendly URLs.
- Optimize URL structure for readability and relevance.
- Avoid dynamic parameters whenever possible.
- Canonicalization:
- Implement canonical tags to specify preferred URLs for indexing.
- Resolve duplicate content issues by setting canonical URLs.
- Internal Linking:
- Create a logical site structure with clear navigation.
- Use descriptive anchor text for internal links.
- Ensure a balanced distribution of internal links throughout the site.
- Schema Markup:
- Implement structured data markup to provide context to search engines.
- Use Schema.org vocabulary to mark up important elements such as products, reviews, and events.
- Test structured data using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
- Page Speed Insights:
- Regularly monitor and optimize page speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Address issues identified by PageSpeed Insights to improve user experience and search engine rankings.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Regularly audit and monitor website performance and technical health.
- Stay updated with industry trends and algorithm changes.
- Continuously optimize and refine technical elements to maintain search visibility and user experience.
By following this Technical SEO checklist, you can ensure that your website is properly optimized for search engines, leading to improved rankings, increased traffic, and better user experience.
How to check whether a url is indexed by Google?
You can check whether a URL is indexed by Google using the following methods:
- Google Search: Simply enter the URL into the Google search bar and hit Enter. If the URL is indexed, it should appear in the search results.
- site: Operator: Use the “site:” operator followed by the URL (without spaces) in the Google search bar. For example, type “site:tajotec.com/technical-seo” to check if “tajotec.com/technical-seo” is indexed.
- Google Search Console: Sign in to Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) and navigate to the “Coverage” report. Here, you can see the indexed status of individual URLs on your website.
- Fetch as Google: In Google Search Console, use the “Fetch as Google” tool to submit the URL for indexing. After fetching, you can check if the URL has been indexed.
- Check Cached Version: Search for the URL in Google and click on the small green arrow next to the search result. Then, select “Cached” to view the cached version of the page. If the page is cached, it’s likely indexed.
- SEO Tools: Various SEO tools, such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz, offer features to check if a URL is indexed. Enter the URL into the tool’s search bar to see its indexed status.
By using these methods, you can determine whether a specific URL is indexed by Google and take appropriate actions if necessary to ensure proper indexing.
How to block a url from being indexed?
To block a URL from being indexed by search engines like Google, you can use the following methods:
- Robots.txt File:
Add a “Disallow” directive to the robots.txt file to instruct search engine crawlers not to index specific URLs or directories. For example:

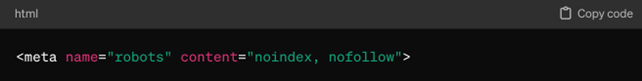
- Meta Robots Tag:
Add a meta robots tag to the HTML header of the page you want to block indexing. Use the “noindex” attribute to prevent search engines from indexing the page. For example:

- X-Robots-Tag HTTP Header:
Set the X-Robots-Tag HTTP header in your web server configuration to specify noindex directives for specific URLs. For example:

- Google Search Console (URL Removal Tool):
Use Google Search Console to temporarily remove URLs from Google’s index. Navigate to the “Removals” section and enter the URL you want to remove. Keep in mind that this method is temporary and will only hide the URL from search results for about 90 days.
- Canonicalization:
Set a canonical tag on the page you want to block indexing, specifying the preferred URL that should be indexed instead. This doesn’t directly block indexing but can help consolidate indexing signals to the preferred URL.
Choose the method that best suits your needs and implement it accordingly to block specific URLs from being indexed by search engines. Keep in mind that these methods may not completely prevent all search engines from indexing the URL, but they are effective for most cases.
What is a website crawler?
A website crawler, also known as a web spider, web robot, or web crawler, is an automated program or script that systematically browses and indexes web pages on the internet. Crawlers are used by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo to discover and collect information from web pages, which is then indexed and made available in search engine results.
The primary function of a website crawler is to traverse the internet, following hyperlinks from one web page to another, and gathering data about the content and structure of each page it visits. This process, known as crawling or spidering, allows search engines to create an index of web pages, which is then used to respond to user queries with relevant search results.
Website crawlers work by sending HTTP requests to web servers, retrieving HTML content from web pages, and parsing the HTML to extract information such as text, links, metadata, and other elements. The crawler then stores this information in a database, where it can be analyzed, indexed, and retrieved in response to search queries.
Overall, website crawlers play a crucial role in the operation of search engines, enabling them to organize and present vast amounts of information from the web in a structured and searchable format.
Here’s an example of how a website crawler, such as Googlebot, might traverse and index web pages:
- Googlebot starts by visiting a seed URL, such as “https://www.example.com”.
- Upon reaching the seed URL, Googlebot retrieves the HTML content of the page.
- Googlebot parses the HTML content to extract links to other pages on the website, such as “https://www.example.com/page1” and “https://www.example.com/page2”.
- Googlebot follows these links to visit and retrieve the HTML content of the linked pages.
- This process continues recursively, with Googlebot discovering and visiting more pages by following hyperlinks.
- As Googlebot crawls each page, it extracts and indexes relevant information, including text content, metadata, images, and other elements.
- The extracted information is then stored in Google’s index, where it can be retrieved and displayed in search results when users search for relevant queries. 8. Periodically, Googlebot revisits previously crawled pages to check for updates and ensure the index remains up-to-date.
This example illustrates how a website crawler systematically traverses the web, discovering, and indexing web pages to provide relevant and accurate search results to users.
Ready to optimize your website?